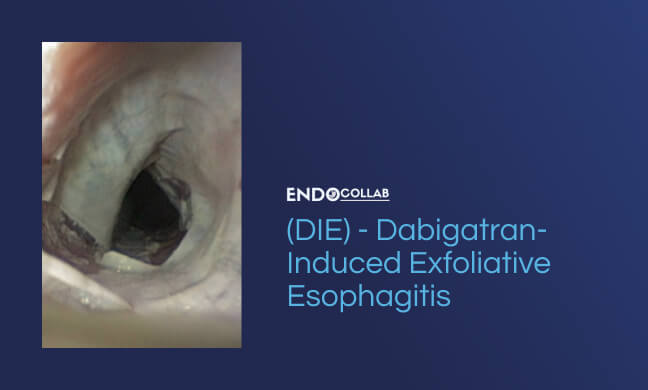
Non-vitamin K anticoagulants (NOAC), also known as direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) are now commonly used for a variety of conditions requiring chronic anticoagulation. The dabigatran pellets are covered with a tartaric acid core. This strong acid may result in squamous epithelial damage with ensuing exfoliative esophagitis. Elderly patients are more prone to suffer esophageal damage due to medications as they have a) decreased salivary production, b) may not drink enough fluids and c) often have esophageal dysmotility. All these factors contribute to prolonged contact of medications with the esophageal mucosa.
Other important causes of exfoliative esophagitis are: Herpes simplex Virus infection (A), esophagitis dissecans superficialis due to medications(biphosphonates, dabigatran, sunitinib) (B, C), graft-versus-host disease(GVHD), amyloidosis, pemphigus vulgaris.
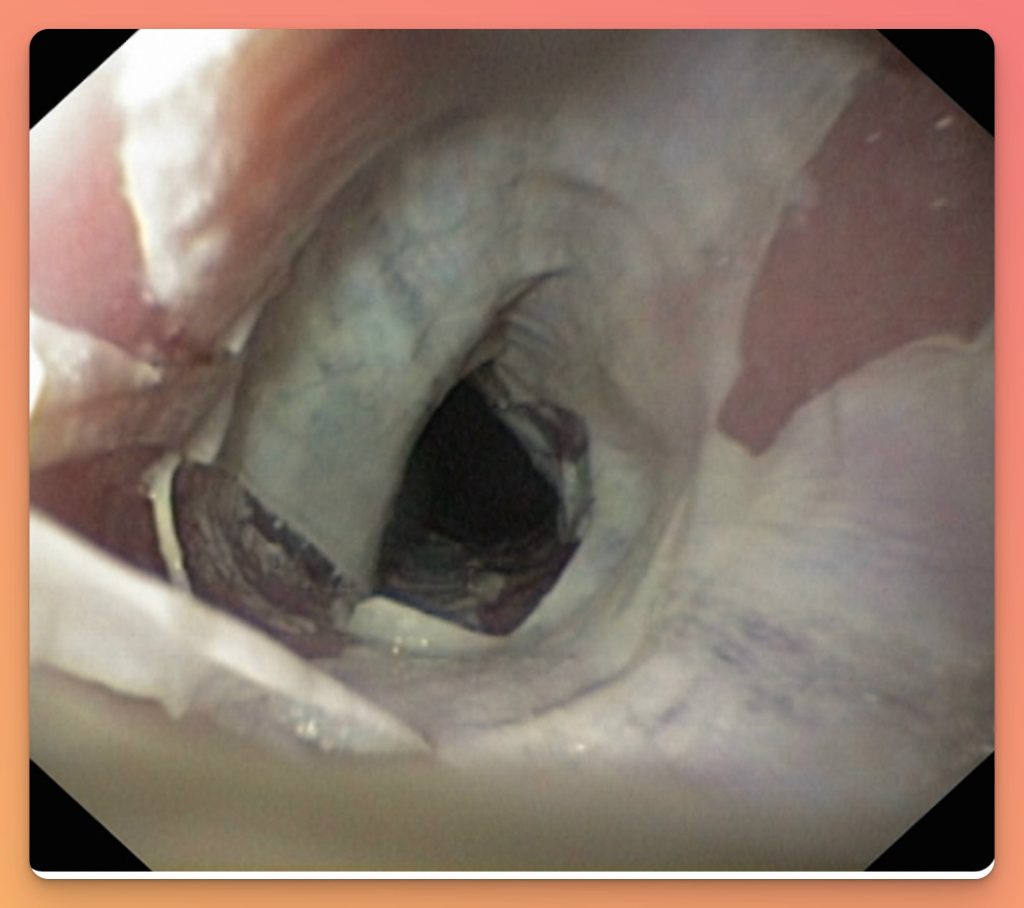

In a study looking at 91 patients in dabigatran who underwent endoscopy Toya el al. found that
A) Dabigatran causes the esophageal mucosal injury in up to 20% of patients.
B) Of the 19 patients with the esophagitis, 18 (94.7%) showed longitudinally sloughing, epithelial casts in the mid and/or lower esophagus
C) 70% of patients with dabigatran induced esophagitis had symptoms.
Ref: Toya Y, Nakamura S, Tomita K, et al. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis: The prevalence and endoscopic characteristics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:610-4.